The rapid development of drone technology, while driving innovations in fields such as aerial photography, logistics and agriculture, has also brought about major challenges such as illegal intrusion, privacy violation and security threats. For instance, in 2024, a certain international airport suffered flight delays due to drones illegally entering no-fly zones, resulting in economic losses amounting to several million dollars. This highlighted the urgent need for drone security systems. The unmanned Aerial vehicle (UAV) security System (also known as the anti-UAV system, C-UAS, or Counter-Unmanned Aerial System) integrates detection, interference, capture, and command and control technologies to form a complete defense chain from discovery to disposal, effectively responding to the threat of illegal UAVs. This article will provide a detailed introduction to the composition and value of the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) security system from four aspects: the core technical composition, system functions and roles, practical application scenarios, and future development trends, revealing how it provides comprehensive support for public safety and airspace management in complex environments.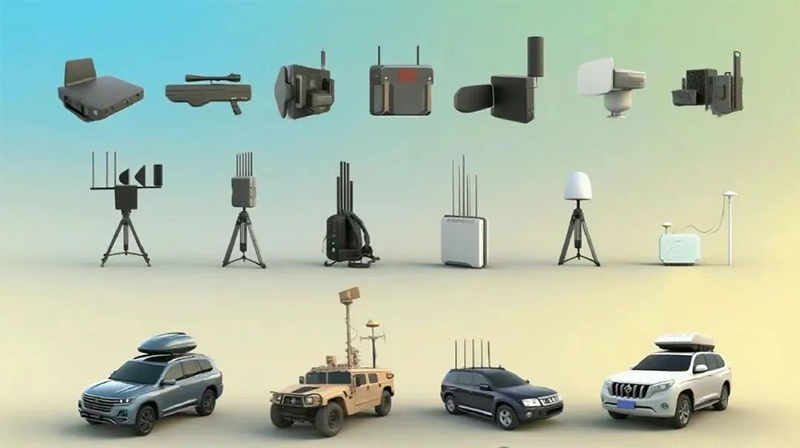
一. Core Technical Components of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Security Systems
The unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) security system works in coordination through multiple technical modules to achieve detection, tracking, suppression and handling of UAVs. Its core technologies include detection systems, interference systems, capture systems and command and control systems.
Detection System: The "Eyes" for Perceiving and locating Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
The detection system is responsible for identifying and locating unmanned aerial vehicles and serves as the first line of defense in the security system. The core components include
Radar system: Utilizing millimeter-wave or microwave radar, it detects the position, speed and trajectory of unmanned aerial vehicles, covering 5 to 15 kilometers with a positioning accuracy of 0.5 meters. It is suitable for low-altitude or complex terrain.
Photoelectric/infrared sensor: Through 4K camera and infrared thermal imaging (sensitivity <40mK), it captures the visual and thermal features of the unmanned aerial vehicle, with a detection range of 2-5 kilometers, suitable for night or foggy days.
Acoustic wave detector: It analyzes the acoustic characteristics of propellers through a microphone array, with a detection range of 500 to 1000 meters, suitable for urban environments.
The detection system supports multi-sensor fusion, is equipped with a servo motor to achieve 360° coverage, and the data fusion algorithm enhances the detection accuracy.
Interference system: A "barrier" for Suppressing Drone Signals
The interference system cuts off the communication and navigation functions of the unmanned aerial vehicle by emitting electromagnetic signals. The core components include
Rf jammer: Emits white noise or sweep frequency signals, suppresses 2.4GHz and 5.8GHz frequency bands, with power ranging from 10W to 500W, covering a range of 500 meters to 10 kilometers. For instance, a 100W jammer can force a drone to land within a range of 5 kilometers.
GPS jammer: Targeting the 1.5GHz GPS L1 frequency band, it emits noise or false signals, disrupting positioning and covering 1 to 5 kilometers. For instance, false signals can induce drones to fly towards designated areas.
Portable interference gun: Handheld device, power 10-50W, coverage 500-2000 meters, equipped with directional sky line(gain 10-15dB) and laser sight, suitable for rapid response.

The interference system adopts Software Defined Radio (SDR) technology, supports frequency band expansion (such as 6GHz Wi-Fi), and is equipped with a spectrum analyzer to adjust signal parameters in real time.
Contact: jack
Phone: +8618027668735
Tel: whatsapp:+8618027668735
E-mail: jack_hlxt@163.com
Add: Room 14150, Haowei Technology Building, No. 2 Nanba Road, High-Tech Industrial Development Zone, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, China.